What does ACAT mean?
This is the acronym for the “Analogous Comparison and Transfer” Method. This pedagogical approach to teaching STEM subjects was developed by Peter Mazohl (EBI/EIE Austria) and published at the ICERI 2017 (International Conference for Education, Research, and Innovation in Seville).
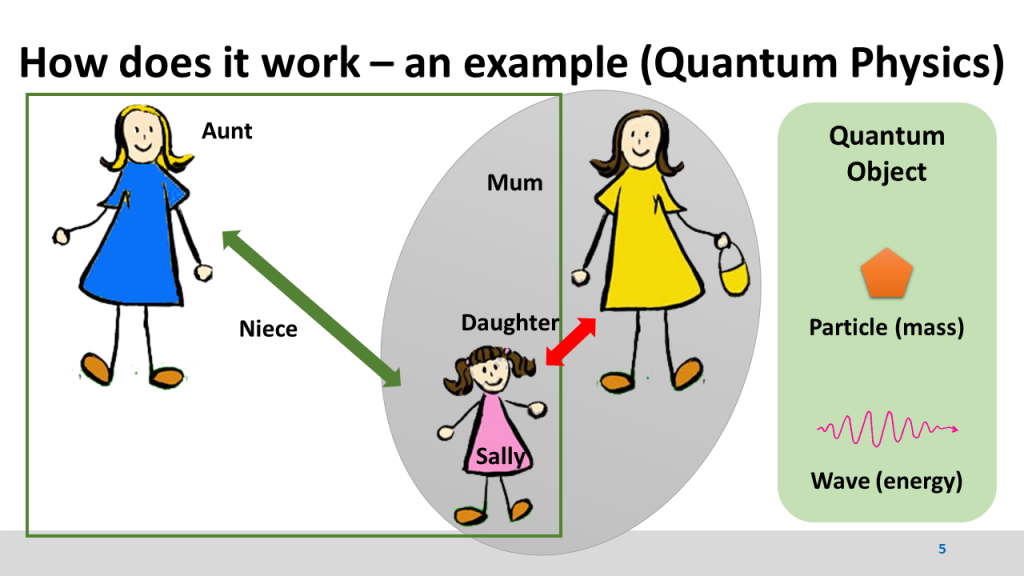
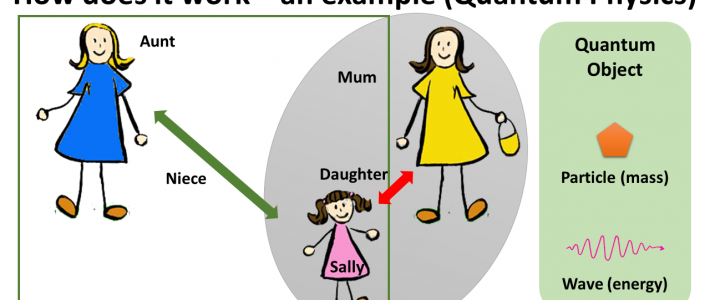
This method means a new pedagogical approach to strengthen female learners in STEM subjects. The method was developed in School Education and focuses on the age of 16 to 18 years old students. The method uses analogous comparisons by taking examples or situations from everyday life and in consequence the logical or analogous transfer to the scientific problem. The method uses the development of imaginations or “pictures in the head” to develop a view of the analogy; this picture is transferred as a problem-solving idea to the concrete scientific problem. Multimedia material like animations are used to provide a higher level of imagination and to develop the understanding for the discussed problem. The method was developed in the disciplines physics, mathematics and computer science and was tested in physics at high school level.
It turned out that male learners also benefit from this approach and get a deeper understanding in the fields of science.
To proof the ACAT method and to test the usability and get some reference to the published study an ERASMUS+ KA2 School Project was started (with December 2018). The project’s outcomes will be several examples of the implementation of the ACAT method, tested and evaluated in a Spanish, an Irish, and finally in a Swedish school.









 Books are still available – Amazon started the business success by selling books (and still sells them), libraries are still used intensively by people borrowing books there. Masses of books – in small quantities – are published and printed as “book on demand”.
Books are still available – Amazon started the business success by selling books (and still sells them), libraries are still used intensively by people borrowing books there. Masses of books – in small quantities – are published and printed as “book on demand”.





